Class 8 Math Comparing Quantities Notes
Comparing Quantities – Class 8
Hi kids! This chapter is all about Comparing Quantities. We’ll learn how to use percentages, calculate profit and loss, and understand simple interest – all things we use in everyday life!
1. Percentage
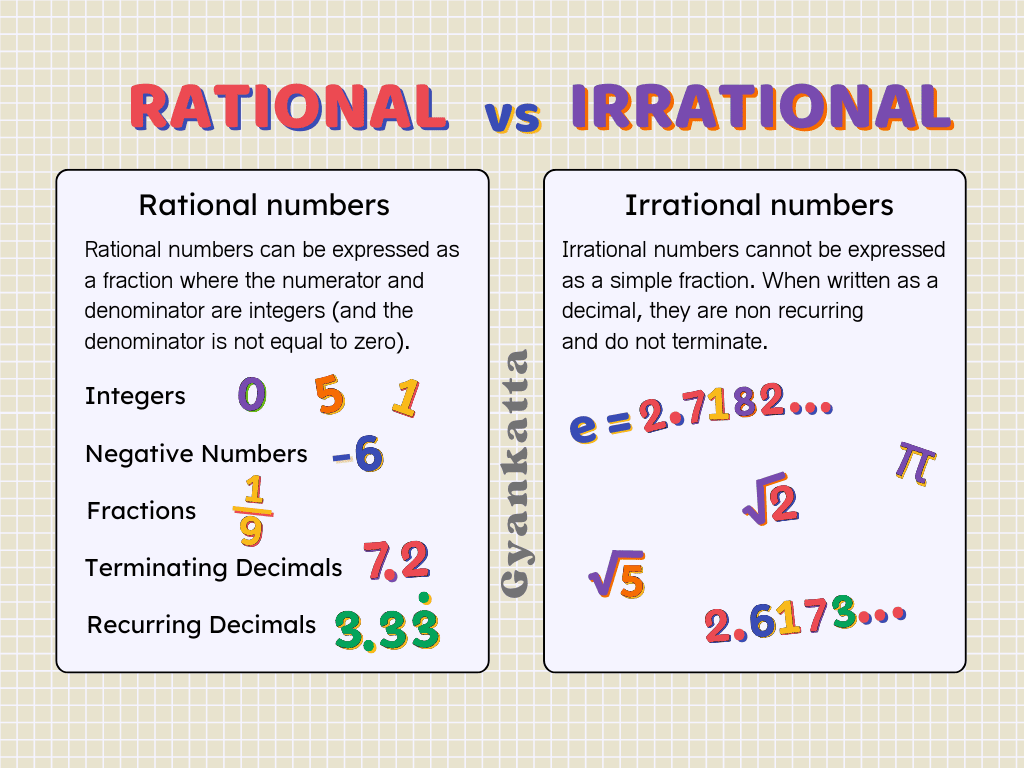
A percentage is a way of expressing a number as a fraction of 100. The word “percent” means “out of 100”. We use the symbol %.
Example: 25% means 25 out of 100, or 25/100, which can be simplified to 1/4.
Converting Fractions to Percentages:
Multiply the fraction by 100.
Example: 1/2 = (1/2) * 100 = 50%
Converting Percentages to Fractions:
Divide the percentage by 100 and simplify.
Example: 75% = 75/100 = 3/4
Example: If a shirt costs Rs. 500 and is on sale for 20% off, the discount is (20/100) * 500 = Rs. 100. The sale price is Rs. 500 – Rs. 100 = Rs. 400.
2. Profit and Loss
These terms are used in business to describe whether money is gained or lost in a transaction.
- Cost Price (CP): The price at which an item is bought.
- Selling Price (SP): The price at which an item is sold.
- Profit: SP > CP. Profit = SP – CP
- Loss: SP < CP. Loss = CP – SP
- Profit Percentage: (Profit / CP) * 100
- Loss Percentage: (Loss / CP) * 100
Example: A shopkeeper buys a toy for Rs. 200 and sells it for Rs. 250. The profit is Rs. 250 – Rs. 200 = Rs. 50. The profit percentage is (50/200) * 100 = 25%.
3. Simple Interest
Simple interest is a method of calculating interest on a principal amount. It’s calculated only on the original principal.
- Principal (P): The original amount of money.
- Rate (R): The percentage of interest per year.
- Time (T): The number of years.
- Simple Interest (SI): (P * R * T) / 100
- Amount (A): P + SI
Example: If you deposit Rs. 1000 in a bank at a simple interest rate of 5% per year for 3 years, the simple interest earned is (1000 * 5 * 3) / 100 = Rs. 150. The total amount after 3 years will be Rs. 1000 + Rs. 150 = Rs. 1150.
These concepts are essential for understanding financial transactions, business deals, and many other real-world situations.
Comparing Quantities Quiz – Application Problems
1. Discount: A shopkeeper offers a 20% discount on a dress marked at Rs. 1500. What is the sale price of the dress?
2. Profit: A fruit seller buys 10 kg of apples for Rs. 400 and sells them for Rs. 50 per kg. What is the profit percentage?
3. Simple Interest: Rohan deposits Rs. 5000 in a bank at a simple interest rate of 6% per annum for 2 years. How much interest will he earn?
4. Percentage Increase: The population of a town increased from 20,000 to 25,000. What is the percentage increase in population?
5. Loss: A shopkeeper sells a chair for Rs. 800, incurring a loss of 20%. What was the cost price of the chair?
6. Percentage Decrease: The price of a car decreased from Rs. 500,000 to Rs. 450,000. What is the percentage decrease in price?
7. Profit and Loss: A vendor buys 5 dozen bananas for Rs. 200. He sells each banana for Rs. 5. What is his profit or loss percentage?
8. Simple Interest Calculation: What principal amount will earn Rs. 900 as simple interest in 3 years at a rate of 5% per annum?
9. Successive Discounts: A shop offers a 10% discount followed by a 20% discount. What is the equivalent single discount?
10. Commission: A salesperson receives a 5% commission on all sales. If they sell goods worth Rs. 20,000, what is their commission amount?